Hemp Laws by state
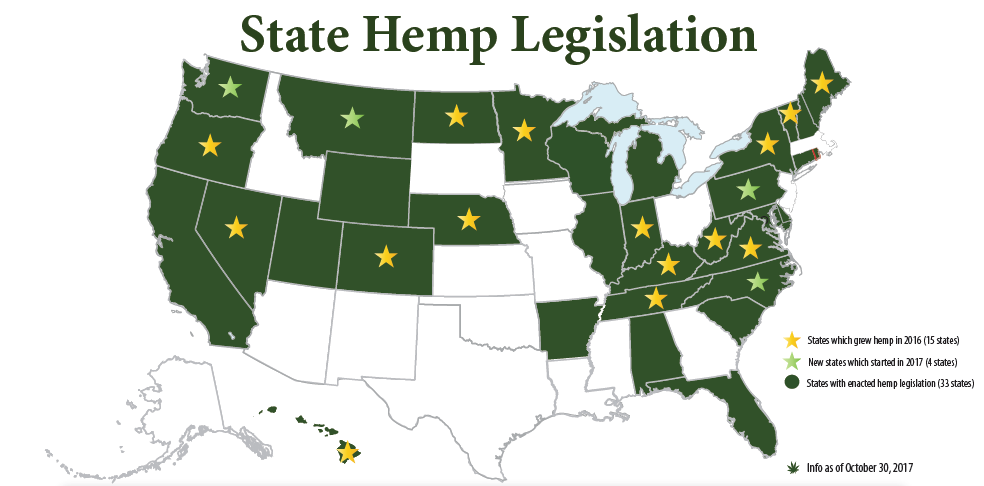
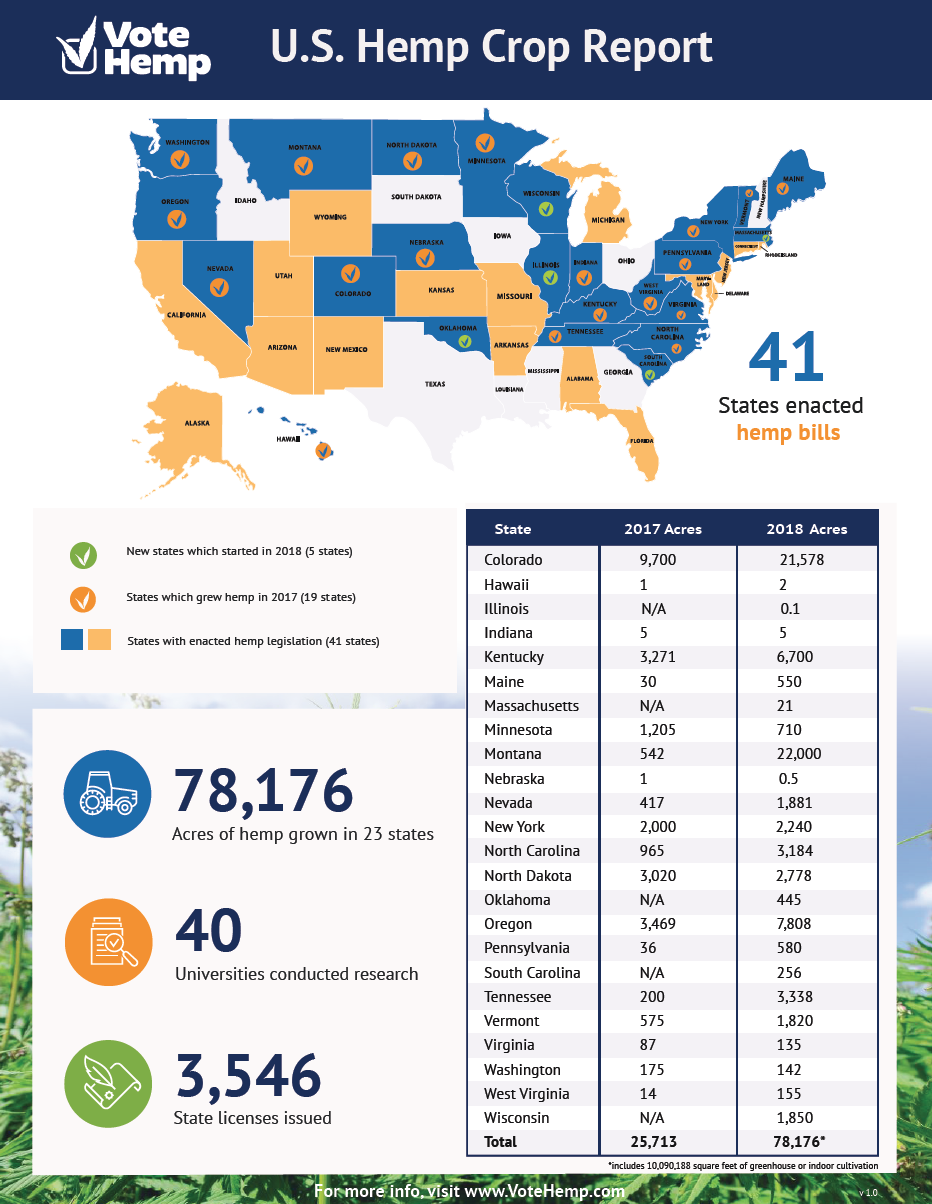
The table below lists all states in alphabetical order which have Industrial Hemp laws that pertain to the governance and cultivation of Industrial Hemp within that state. We have provided a link to the states program for Industrial Hemp through that states respective Department of Agriculture. There you will find information regarding regulation, zoning, certified seed programs, and forms needed for registration with the state. Thus far, 48 states have passed laws regulating Industrial Hemp within their department of Agriculture pages.
The (Agricultural Improvement Act of 2018) Farm Bill amends the Agricultural Marketing Act of 1946 (AMA) to categorize hemp as an agricultural commodity regulated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Agricultural commodities are eligible for a range of federal programs including crop insurance, research grants, and certification of organic production practices. The Farm Bill also removes hemp from the Controlled Substances Act’s (CSA) list of controlled substances, and creates requirements for hemp “plans” administered by individual states or tribal governments. Section 297A of the 2018 Farm Bill redefines the term “hemp” so that the dividing line between hemp and marijuana is the THC level. As the language states: “The term 'hemp' means the plant Cannabis sativa L. and any part of that plant, including the seeds thereof and all derivatives, extracts, cannabinoids, isomers, acids, salts, and salts of isomers, whether growing or not, with a delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol concentration of not more than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis.” Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 Sec. 297A Later in the act under Section 12619 it revises the Controlled Substances Act to specifically exclude “hemp as defined in section 297A of the Agricultural Marketing Act” from being a Controlled Substance. Thus, a cannabis sativa plant that is less than 0.3% THC and all of its associated parts (including all cannabinoids and extracts) are excluded from the Controlled Substances Act as hemp.
You may also find more information regarding federal and state regulation at Hemp State Laws